Can I Read Posts On The Internet Lightning Speed ? Yes.
can I read posts on the internet lightning speed ? yes.
can I read a scientific publication quickly ? also yes !!!
now, can I read a normal book at a somewhat regular speed ? no, I have to re-read the previous page, hell the previous chapter because I forgot what the conversation between the character was about !
More Posts from The-maddest-robot and Others

Picture of IC59 and IC63. This is a pair of nebula located near the star γ Cassiopeia, the big star at the bottom, which is responsible for making the nebula glow. Both nebula are composed of ionise hydrogen responsible for the red colour (especially on IC63) and colder dust/gas responsible for the blue colour (most visible on IC59). γ Cassiopeia can make taking photos of those nebula difficult due to the halos it produces, I did my best to limit its impact during processing, but there is still a faint blue halo around it. IC63 is also known as the Ghost of Cassiopeia due to its shape, it was discovered in 1893 by the German astronomer Max Wolf.
Image taken using a CarbonStar 150/600 newtonian telescope with a 0.95 coma corrector, ZWO ASI294 monochrome camera. 12x300s image for each filter (LRGBHa), total imaging time 5h, stacking and processing done in PixInsight. Details of both objects: IC63

IC59


This is M51, also known as the Whirlpool Galaxy it is a pair a galaxy currently interacting together. If you look at the two arms of the spiral, you will see that the one on the left is somewhat deformed (near the other galaxy) this is due to the gravitational interaction between the two galaxies. Those interaction are also the reason why the left galaxy (NGC 5195) is this irregular. Some of the models have proposed that both galaxies have passed through each other at some point in the past. In the future both galaxie will slowly fuse together, but this will take at least a few hundred million years. Multiple other interacting galaxies also exist, such as the butterfly galaxies or the antenna galaxies.
This photo was supposed to be a test of my new equatorial mount but the result was WAY BETTER than expected so here you go (the post-treatment of the photos is not the best ever but I had to work with a limited amount a data). I will probably post more photos this summer since I now have access to better skys and a better mount than in Munich (If the weather complies).
Skip Google for Research
As Google has worked to overtake the internet, its search algorithm has not just gotten worse. It has been designed to prioritize advertisers and popular pages often times excluding pages and content that better matches your search terms
As a writer in need of information for my stories, I find this unacceptable. As a proponent of availability of information so the populace can actually educate itself, it is unforgivable.
Below is a concise list of useful research sites compiled by Edward Clark over on Facebook. I was familiar with some, but not all of these.
⁂
Google is so powerful that it “hides” other search systems from us. We just don’t know the existence of most of them. Meanwhile, there are still a huge number of excellent searchers in the world who specialize in books, science, other smart information. Keep a list of sites you never heard of.
www.refseek.com - Academic Resource Search. More than a billion sources: encyclopedia, monographies, magazines.
www.worldcat.org - a search for the contents of 20 thousand worldwide libraries. Find out where lies the nearest rare book you need.
https://link.springer.com - access to more than 10 million scientific documents: books, articles, research protocols.
www.bioline.org.br is a library of scientific bioscience journals published in developing countries.
http://repec.org - volunteers from 102 countries have collected almost 4 million publications on economics and related science.
www.science.gov is an American state search engine on 2200+ scientific sites. More than 200 million articles are indexed.
www.pdfdrive.com is the largest website for free download of books in PDF format. Claiming over 225 million names.
www.base-search.net is one of the most powerful researches on academic studies texts. More than 100 million scientific documents, 70% of them are free

II took another photo of M51 / the whirlpool galaxy, same camera and same processing of the data, but I used a different (bigger) telescope. Here, using a bigger telescope has two major effects, firstly the image is more ''zoomed in'' since the focal length is longer. Secondly, since the diameter is bigger the maximal (angular) resolution of the image can be increased. This increase in resolution is due to the way the waves of light are diffracted by the aperture of the optical instrument (in short bigger aperture = better resolution). This increase in resolution is one of the reasons professional telescopes have gigantic mirrors and/or use telescope arrays combined with interferometry to increase their maximal angular resolution.

I took another photo of the crescent nebula (C27) this time using my monochrome camera and processed similarly to my photos of the veil nebula. The H-alpha photos really helped to enhance the ionised hydrogen present in this region of space (deep red clouds in the background). Still not completely satisfied with how the stars turned out (too much halo visible around them), could have been mitigated if the clouds had not come half way through the imaging session or if I do another night of imaging of this target.

This is a picture of the hydrogen and dust cloud surrounding the star Sadr (the bright white dot near the center) also known as IC 1318. The bright parts represent hydrogen clouds and the dark parts dust clouds. Those types of clouds are the birthplace of new stars. This particular photo is in black and white because it was made by using a filter that lets only the light emitted by ionised hydrogen (the H alpha spectral line) pass through it. This increases the visibility of the hydrogen clouds. Since this light is at 656 nm, it would appear bright red if coloured. Together with H beta (496 nm) also from hydrogen and O III (around 500 nm) from oxygen both cyan in color, they represent the majority of light emitted by gas clouds. So in conclusion if you were able to see this gas cloud directly it would appear a reddish-magenta color (H alpha being the dominant emission).
sometimes astronomy camera companies will post about their horrible attempts to fix hardware problems with software. normally these are unremarkable.

and then sometimes they contain a beautiful single sentence that will live in your brain forever

For those not in the US wanting to search for dark skies near you, this website is quite useful.
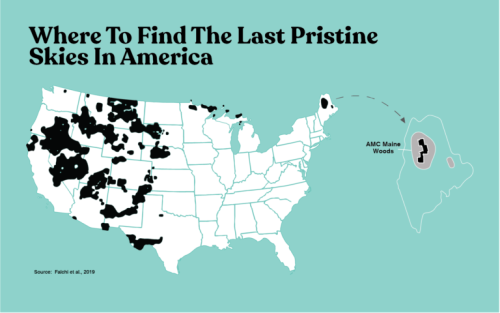
The black areas represent the remaining natural dark skies in the United States
Just got a week of clear weather will I had access to my telescope, managed to get a good amount of data, treatment will have to wait though (I have some exams in 2 weeks). In the meantime, here's a quick test I did with the horse head nebula.

This is a SHH composition (there is nearly no OIII emission in this nebula and I did bother imaging in this wavelength).
-
 tarakanpaintedpurple liked this · 10 months ago
tarakanpaintedpurple liked this · 10 months ago -
 apathyneverlandedonthemoon liked this · 1 year ago
apathyneverlandedonthemoon liked this · 1 year ago -
 daltongraham reblogged this · 1 year ago
daltongraham reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 daltongraham liked this · 1 year ago
daltongraham liked this · 1 year ago -
 mckitterick liked this · 1 year ago
mckitterick liked this · 1 year ago -
 the-maddest-robot reblogged this · 1 year ago
the-maddest-robot reblogged this · 1 year ago

Astrophotographer & chemist, mid 20'sCurrently on the roof yelling at the clouds to get out of the wayMostly astrophotos I've taken, possibly other science related stuff
51 posts